Standard log files: Difference between revisions
m (→Added in 1.9.4) |
m (→Added in 1.9.3) |
||
| Line 411: | Line 411: | ||
===Added in 1.9.3=== |
===Added in 1.9.3=== |
||
''For Cumulus MX reading a line created by Cumulus 1'', all the |
''For Cumulus MX 3.6.x reading a line created by Cumulus 1'', all the remaining fields will be '''filled with exactly one space''', and editing that to an empty string will be rejected. Cumulus MX before version 3.6.0 cannot read a log file with all lines in that log file created by any Cumulus 1 version prior to 1.9.4. |
||
{| border="1" class="wikitable" |
{| border="1" class="wikitable" |
||
Revision as of 15:15, 19 June 2020
Introduction
This article is about the standard logging file that stores the full set of current (read and derived) values at whatever interval you have set for Cumulus to keep detailed logging. The default time between data logging lines is every 10 minutes, but you can change this:
- Cumulus 1: From Configuration menu, select the station settings screen, Data log interval box on extreme RH side.
- Cumulus MX: From settings tab, select the Station settings screen, and find Log interval after the Ecowitt GW1000 Settings section.
These files are automatically created with names in the form <Month><Year>log.txt (for example, the file for August 2009 is often called Aug09log.txt), but the month can be in another language or a different abbreviation depending on your locale. There is no setting to change this format.
The standard logging file is in comma-separated format with one line per entry. Being comma separated does not mean the fields in this log are always separated by commas, they might use semi-colon (;) for example.
There is an equivalent logging file for extra sensor values. In fact, in Cumulus MX, the processing of this extra sensor logging file shares a lot of the code with the processing of the standard logging file, as they both are updated at same interval, and they both take values processed following a read from your weather station. The applications programming interface (api) that sends values between the MX engine and the MX admin interface is also identical (with a parameter "Extra" that swaps between true and false depending on the log file involved).
There is another logging file, speciallog.txt, for detailed logging of internal temperature and humidity, but it is not split into separate files for each month. Although this exists in Cumulus 1, it appears this functionality is missing from MX.
File content
This file has one line added each time the Cumulus timer says the logging interval has passed.
All data is logged in the units as selected by the user:
- Cumulus 1: From Configuration menu, select the station settings screen, Units box is just below the centre of that screen.
- Cumulus MX: From settings tab, select the Station settings screen, and find Units section at the start of that screen.
Each line has a number of fields separated by whatever symbol is defined as the list separator on your device, typically a comma (,) or a semi-colon (;).
- The various fields are all listed later in this article, but they can be of various types:
- Date, this is always the first field, and it always uses a fixed format, ignoring the format defined in your locale.
- Time, this always the second field, and is always in the form hh:mm (Cumulus will not be able to understand the file if you edit the time to a format that includes seconds) using the 24 hour clock and local time (system time). However, if you use the feature in MX to upload the equivalent of this file to a database table, the automatic update upload will add ":00" to include seconds.
- Note that it is perfectly possible to have two successive lines in a standard log file with same time, although this should not happen in normal running, it can result from a hiccup or other interference on your device. If you are asking MX to upload the contents of this file, a second line with same time is ignored, only the first line with a particular date and time is uploaded.
- All Remaining fields are spot values, either what has just been read from your station, or a derived value calculated from a set of values read from your station. For these value fields, Cumulus may have converted from the unit used by your weather station to the unit that you have requested to use, and there will be some inaccuracy inevitable in such conversions. Where the value to be stored is a real number with decimal places, Cumulus will use a decimal comma or decimal point depending on which is defined in your locale, do be careful not to change that locale if you need to change your device or update it, as Cumulus can only read files where the same decimal separator is used everywhere.
For more information on these files see in the Cumulus help file, in the section “The Data log file”. This is installed with Cumulus 1, but can be read with Windows after downloading from Software#Resources page in this Wiki.
Accessing the Standard Log File
Access to current log by other processes
As the log file for the current month will be updated frequently by Cumulus (when it is running), Cumulus 1 applies an exclusive lock, and (as explained further below) conflicts can happen if another process seeks to access this file. Consequently don't let your antivirus scans access this file, nor try to edit it outside Cumulus while Cumulus is running.
Also note these log files do not include a header line, and should not be edited to include it.
The appropriate header file for the standard data logs can be found for any installed version of Cumulus by looking for "monthlyfileheader.txt", in the directory above the 'data' directory containing the standard log. The viewing screens for the two flavours, as described next, automatically include the header line above the tables they show.
A full discussion of the problems with conflicts of access to the standard log file can be found in this support forum topic.
Viewing the standard log file in Cumulus 1
In the View menu of Cumulus 1, select Data logs, click Load....
The standard Windows File Select dialogue is displayed for the 'data' subdirectory of the Cumulus installation directory.
Select the required month for which to display the standard log, click Open and you will see the contents in a neat table with column headings, rows striped, and the date/time on a lighter background. This is a text viewer, and works best when at full screen, but even then you are likely to need to scroll both horizontally and vertically to look at all the figures. If you click on an individual figure the cell will be highlighted, but you cannot edit the figures on a view screen. Cumulus 1 does not provide an editing facility for this file.
Problems in Cumulus 1
If no logs seen, see FAQ: I can't find my data files. Also note, this Data logs viewer is only for viewing standard log files (not any other files in the same data directory), the column headings for standard (monthly) log files will always be shown at the top of the screen.
Editing for Cumulus 1 users
Cumulus 1 allows you to view any standard log file, but not to edit the contents. Consequently for Cumulus 1, you need to edit standard log files outside Cumulus 1, subject to the following rules:
- You can't edit the current log file while Cumulus 1 is running, because Cumulus needs exclusive write access. You can edit the log file for a past month, unless you are looking at past months using Cumulus editors.
- You can't edit any log file with a word processor, as they add control characters and other information that Cumulus cannot understand.
- You can use either a specialised comma separated value file editor or a text editor.
- Text editors designed for programmers will allow you to select the encoding (Cumulus will be confused by any Byte Order Mark, so select the encoding type without BOM).
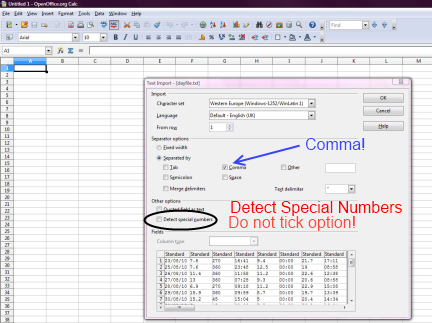
- If you choose to use a spreadsheet, ensure that all columns are treated as normal text, do not let (don't accept Excel default) the spreadsheet recognise the first field contains a date as it will convert that column into a number (e.g. days since 1900 or days since 1970). For example in Libre Office make sure that "Detect special numbers" is not selected. Many spreadsheets will offer a CSV option for saving the file (in Libre Office tick "Edit Filter Settings" on "save as ...").
- If you amend a field, ensure that replacement is same format as original (same decimal separator if not integer).
- Ensure no blank lines, and if you have added in the column headings then remove that heading line when saving ready for Cumulus.
You can see #Manipulation outside Cumulus below for more information.
The viewing and editing web page in admin interface of Cumulus MX
In the admin interface, there is a "Data Logs" tab, from it select Data logs.
- On this screen,you see a box for selecting the log you want to display. The default month and year (shown on loading the web page) is taken from yesterday's date. No log is loaded at start up. You can either type in a period (one or two digit representing month, then hyphen, then four digits representing year) or select year then month in the data picker (this is produced by the bootstrap software MX uses, it is not the date picker provided by your browser), when you click on the month the box is updated with selected period.
- Next to it is a "Load" button. Press it and the Cumulus MX engine will generate an application programming interface (api) table that will appear on the web page using dataTables software. There is a "Refresh" button, for when you want that api to refresh the table (without reloading the whole page).
No conflict
Because the dataTables version of the log seen on this web page in the admin interface, is not the actual log being used by the MX "engine", there can be no conflicts on access and this way of editing log files is just as safe for the current log as for past logs.
Additional ideas for how any Standard Log File can be used within Cumulus
Uploading current log to your web site
The current standard log can be updated at your usual web site update interval using <currentlogfile> as the local file name. If your web site upload interval is the same as the logging interval, there might be a conflict because of the file locking, so this might not work every time. However, extra web files are not processed all at once, so by listing this file against a higher number the chance of conflict is reduced.
- For Cumulus 1, list this log file as the local file by specifying the parameter 'ExtraLocal[0-99]=<currentlogfile>' in Cumulus.ini#Section:_FTP_Site).
- For Cumulus MX, use the Extra web files option within the "Settings" tab, and enter "<currentlogfile>" in the local column.
- You can also use <currentlogfile> as part of the remote file path, as explained in the Cumulus Help. You will also need to specify a path in the remote column for MX or the 'ExtraRemote[0 to 99]=...' for Cumulus 1. You might of course want to specify a local path, and leave the FTP column unticked (or set to 0 for Cumulus 1). You can then use a separate FTP process to upload this copy.
- It is recommended that you do not try to FTP the actual standard log file (instead FTP a copy) because the FTP process is relatively slow, particularly as the file size increases as the month progresses, so there is an increasing chance of conflict with logging the next line of values - see support forum here for more information.
- An alternative approach is to upload the standard log file just once a day, at a quiet period such as an odd number of seconds after quarter-past midnight using a process scheduled outside Cumulus.
Cumulus 1: transferring the contents of the standard log file into a database table
- A script can be used to read the your copy of the standard log file into either a database table (see ImportCumulusFile), or into an array, for further processing.
- It is, as advised above, best to work with a copy of the file that Cumulus is actually updating, because there can be a conflict of the locks, Cumulus needs to have exclusive use when it does its normal update.
- But this script can safely be used with older standard log files, or a copy of the latest standard log file.
Cumulus MX: transferring the contents of the standard log file into a database table
Although the ImportCumulusFile script can be used with MX too, MX provides 2 other ways to transfer the contents of a Standard Log File into a database table.
- The first, uploads ALL past data, using ExportMySQL.exe found in the top level folder where CumulusMX.exe is found. It can be run using the same way as you run the main program, but you need to specify "monthly" as the first parameter (this indicates the table name that is to be updated, it does not work for any other table name).
- The second, which only uploads the line most recently added to the standard log file is found in the My SQL settings section of the admin interface. Find more information at MySQL settings. In this option the default table name is "monthly", but it can be changed.
After you have edited (or created any missing) Standard log files, you can:
- HOW TO CORRECT HIGHS AND LOWS IN CUMULUS 1
- update the highs and lows in Alltime.ini by choosing all time records from the Edit menu. See Alltimelog.txt for current and previous values.
- update (if the created/edited standard log is within the current year) the highs and lows in year.ini by choosing This year's records from the Edit menu.
- update (if the created/edited standard log is for the current month) the highs and lows in month.ini by choosing This month's records from the Edit menu. See Diags for current and previous values.
- update (from version 1.9.3) the highs and lows in monthlyalltime.ini by choosing Monthly records from the Edit menu. Click the Help button for specific instructions on using Reset and the two Copy column header buttons in this Monthly Records (Highs and Lows) Editor to action all rows.
Note in each of above 4 editing screens you can:
- see the currently stored extremes, and optionally Reset (row by row) to pre-editing value and timestamp.
- load all standard log files, and dayfile.txt to view extremes calculated from those figures (as available) and
- optionally (in Cumulus 1 only) click Copy (row by row) to move the logged values (and associated date/time information) into the relevant .ini file.
- In the MX editor, you need to manually type the numbers read in from the other logs into the output log column.
- (In cumulus 1 only) click the Help button for detailed instructions on using The Records (Highs and Lows) Editors.
- In cumulus 1, store your revised figures by clicking OK (or abandon all your edits by clicking Cancel).
- In MX there are tick and cross options for same effect.
(Each of these screens is a text editor, and works best when at full screen).
- HOW TO USE CORRECTED INFORMATION
- (In cumulus 1 only) see Mean temperatures, Air frosts, Gale days, Rain days, Dry days, and Total Wind run using View menu displays for This month, This period, and This year (These figures are not stored anywhere, nor available as web tags), but Cumulus 1 can calculate these from what it finds in the standard log files and the daily summary log.
- (In cumulus 1 only) use create missing button in the dayfile.txt selection in the Edit menu; This is a text editor, and works best when at full screen. Cumulus will then look through all standard log files and create approximate records for any missing dates in the dayfile if those dates have observations stored in the relevant standard log. (It creates a file in the Cumulus folder called dayfileeditlog.txt which contains the entries it created). Click the Help button for more information. In past and current versions (including 1.9.3), create missing will not affect any records that are incomplete or contain some rogue values (see workaround below).
- obtain (in Cumulus 1 by viewing the created/edited log file) figures needed for manually correcting rogue figures in dayfile.txt. See for example FAQ re correcting rainfall.
- create the relevant monthly and/or annual NOAA style report by choosing NOAA Monthly Report or NOAA Annual Report.
- In Cumulus 1 do this from the View menu, then select the required period using the selectors. Click the Update Display button to see various statistics (including mean temperature) calculated. Generation of complete NOAA reports takes most information from dayfile.txt (based on rollover to rollover meteorological days), except average wind speed and dominant wind direction (both of these it calculates from values read from the standard log files) for period in question. Finally press Save button to store the new or amended report.
- In Cumulus MX, use the Reports tab, then choosing NOAA Monthly Report or NOAA Annual Report. A date selector allows you to choose the exact report you want, click "Load" button next to it. You can alternatively click another button to generate a missing report, or to regenerate an existing report after any corrections you have made to any standard log file relevant to that report. Be aware that a regenerated report might not be quite as accurate as original report which when generated is using figures actually being processed by end of day for the current day.
NOAA Report Notes:
- for obsolete versions up to 1.9.4 build 1085 only: The average wind speed used for NOAA reports and 'This period' type screens was, by a bug, based on midnight to midnight days regardless of rollover time in use. (It is calculated on generation of report or screen from standard log file entries).
- From build 1086, the calculation is based on the rollover time being used.
- For all Cumulus 1 versions, and the MX versions below 3.4.4: the yearly average temperature is calculated from summing monthly maximum and monthly minimum values and dividing by number of values in calculation.
- From version 3.4.4 the annual average temperature is calculated using the integrated method based on every temperature reading processed (it is actually the average calculated from all daily means stored in daily summary log for this year).
Correcting any logged data problems
As already mentioned, it is only MX where the 'Data Logs' screen will allow editing of values in any standard log file, but in both flavours you can use their viewer to look and see if you are happy with what has been recorded.
The MX editor is in the admin interface where it has no access to the actual log file which is stored wherever the MX engine runs. When you ask to load a selected month in that editor, what happens is that the MX engine does a quick read of the log file and puts its contents into the format used by dataTables software. That is what you see on the web page. Subsequently you can select a line there, click the Edit a line button, and the AltEditor software will raise a pop up showing all the fields in the line. This is where you make the edits. When you click the Save edit button, the line is sent back to the MX engine. On arrival of an updated line, the MX engine reads the log file again, into a standard array, replaces the array element corresponding to the received line, writes the array back into log file (replacing previous contents) and regenerates the dataTables format to send back to web page.
Some Weather stations may occasionally supply corrupted or rogue values to Cumulus:
- Cumulus 1 provides via Configuration menu Calibration screen the ability to screen out spikes (i.e. abnormal differences between two successive readings from weather station) in data picked up from some weather stations, it does not work for all types. See Cumulus help screen if you decide to use that to cope with future spikes.
- Cumulus MX provides the same functionality, for the same restricted set of station types in its admin interface.
If a weather station for some reason does not make a new reading available for a particular parameter, then both flavours of Cumulus reuse the same value as before for up to 6 times of reading the other parameters successfully. After that, Cumulus may stop any further processing. By default, Cumulus (of any flavour) will stop any further processing if certain outdoor sensors stop sending information:
- pressure
- wind speed
- temperature
- humidity
Cumulus records in the standard log file various parameters that cannot be obtained from every weather station. Both flavours store zero if no value can be obtained for that parameter.
Some rogue values may be obviously invalid (e.g. a zero pressure), others (e.g. wind shake on a tipping bucket rain gauge on a fine day) may be within the accepted all-time range, but you know the value is not right for that particular time.
You may choose to just edit the rogue value into a reasonable value, or (if you are unable to decide on a better value) to delete that particular entire row in the standard log.
In Cumulus MX you can do both of these in the data logs screen, in Cumulus 1 you will need to use an external editor.
As explained above once any monthly log has been corrected, new highs and lows in other logs are easily rectified.
Spotting rogue values
Frequently, the graphical views (Charts, Graphs or Trends) are the best way to spot many rogue values and to help you guess by interpolation a more reasonable value.
Another possibility is to examine the relevant values in previous versions of the log files stored in the backup or backup/daily subdirectories of where your cumulus executable is stored.
Manipulation outside Cumulus
Any log files for previous months can be edited (outside Cumulus) with Cumulus running, and after editing them, you can do further fetch edits within Cumulus as described above. The standard log file for the current month can also be edited outside Cumulus, but as it is being updated frequently you must stop Cumulus first (that explains why there was no edit option within Cumulus 1!).
Tips -- take a copy of the original log file before you work on it outside Cumulus (perhaps give the not to be touched copy a filename of "<Month><Year>log.csv").
Edit the original file using an editor that treats all fields as text [use either any text editor, a Comma Separated Value editor, or a spreadsheet program that can be instructed not to recognise special field (like date and time) types].
If you wish to use "Calc" in 'Apache Open Office', "Libre Office", or similar, select the field separator you use (in this illustration comma is selected, but your file might use semi-colons between fields, don't select commas if your real numbers use comma between integer and decimal parts) and leave "Detect Special Numbers" unselected (as normal default for this software). Best not to use 'Microsoft Excel' as that normally has opposite default, and may change without any warning the format of all dates so Cumulus can no longer recognise the first two fields:
Important Rules for Cumulus 1
- Each line must contain the fields in correct sequence (since new versions/builds can add to number of fields, Cumulus will accept different months having various row lengths i.e. older ones without the more recent fields at the end).
- The date format uses two digits for the year and should be treated as text. For software (e.g. Excel) with default of recognising formats, ensure that such recognition is turned off, as it is likely to change the dates to either a number representing days since e.g. 31 Dec 1899, or to have four figure years, and then Cumulus will no longer be able to use the log file. (Also the month must be the middle figure, USA convention cannot apply within Log_Files).
- Times in these files are in the form hh:mm using the 24 hour clock and local time (system time). See FAQ#How_does_Cumulus_handle_Daylight_Saving_Time.3F.
- See #List_of_fields_in_the_file to identify if the value you enter for a particular field is an integer (like bearings and humidity values) or a real number (like pressure and rainfall values) in format x.y using your system decimal notation for the decimal point. Fields that accept real number format will also accept integers, but fields expecting integers will not accept decimal points.
- Negative values are allowed for temperatures, all others must be zero or positive. Humidity has a maximum of 99, bearing has a maximum of 360.
- Nulls (',,' if your field separator is a comma, ';;' if your field separator is a semicolon) are not allowed in the row, so if you do not know the value for a particular field within the row, then type in a zero, -999, or 9999 (check the format in the middle column of #List_of_fields_in_the_file and think about the range of numbers allowed for particular fields as per examples in previous bullet). In other words put in an obviously strange number as Cumulus does not have a defined null! This strange number may distort graphs and any calculations, but it will remind you to make a more appropriate guess as soon as you can.
- Note that some fields (e.g. those related to evaporation, UV, solar data) will only contain valid data if your station has the appropriate sensor(s) (without the sensor they contain the default value of zero), but if they apply make sure you note which are stored as integers.
Equivalent rules for MX
- All fields in all lines must contain the same character for separating one field from next and it must be consistent with whatever locale you use when you run MX (it might be set using a parameter to the command running MX, it might be set in Mono, or in Windows control panel).
- Each line must contain all the fields defined in the version of MX that you are using in correct sequence
- Feels like was added onto the end of this log file in version 3.5.4. Any line in any log file produced before you started using MX version 3.5.4 or later will end with Rain since midnight. However, the way that MX was modified for version 3.5.4 means that those earlier lines will be modified by the application process interface used to transfer log lines between the MX engine and the admin interface to include the full number of fields per row and to contain a space character for that additional field. Consequently, any external edit also has to add a field separator and a space to every line where the original lacked feel like.
- The date format uses two digits for the year and should be treated as text. For software (e.g. Excel) with default of recognising formats, ensure that such recognition is turned off, as it is likely to change the dates to either a number representing days since e.g. 31 Dec 1899, or to have four figure years, and then Cumulus will no longer be able to use the log file. (Also the month must be the middle figure, USA convention cannot apply within Log_Files).
- Times in these files are in the form hh:mm using a colon as separator, the 24 hour clock and local time (system time).
- If you are editing a log file that was produced by Cumulus 1 and it used a separator other than a colon (:) then the old separator must be replaced by colon.
- For MX the rules for fields containing values are different to those for Cumulus 1, which makes it difficult to successfully edit any pre MX log files. For MX if a field can take a decimal place, it must contain a decimal figure, and it must use the correct decimal separator as defined in locale. If the field only takes integers (see #List_of_fields_in_the_file) then you cannot edit in any decimal places.
Importing pre-Cumulus data into Cumulus 1
This section was written for Cumulus 1. MX works differently, and all of its processing checks that the value it is processing is after the "start date", so it is not so easy to bring in earlier data. This is discussed further later within this section.
See FAQ: I've just installed Cumulus and it didn't download all the old data from my weather station
Given that standard log files are used as input for updating the all-time, month-by-month alltime (from version 1.9.3), and this year record extremes, for creating missing dayfile.txt entries, and for creating NOAA style reports, you may have some observations from your weather station recorded manually or electronically for a period before you first starting using Cumulus 1 and want to create new standard log files to feed into Cumulus 1.
Here are some issues to consider. There are some postings in the Support Forum about importing past data. Essentially match the fields listed in List of fields in the file below with the fields you have available in your source.
- Dates and times might need some pre-processing (spreadsheet packages usually have ability to select part of a text string and to concatenate a number of strings) to convert them to text in the formats mentioned above. (Note - it is crucial in a spreadsheet to treat the date as text; Do not let the spreadsheet recognise it as a date as it might change the format or store as a 'days since X' number).
- Remember that null values are not allowed within a row, so ensure that you enter an obviously wrong value (-99 or zero might be do) between your operating system defined field separator (normally ',' or ';') and make the row length the minimum shown in the list of fields below. If you use a spreadsheet, treat the file as Comma Separated Value type, but on saving choose the appropriate field separator character (e.g in Libre Office or Open Office 'Save as CSV' select 'Edit Filter Settings').
- Wind directions might be reported as cardinal points (north, south etc) and need converting to bearings in (integer) degrees (spreadsheet packages provide look up functionality to do such conversions).
- Wind speed fields may not directly match to weather station outputs. See #Cumulus_Wind_Speed_Terminology
- Temperature fields may not directly match to weather station outputs. Copy across the fields you can and set the others to -999.99 so they are obvious. See the workaround described below for a way of getting Cumulus to generate (from your newly created monthly logs) apparent temperature, wind chill and heat index to replace any -999.99 figures.
- Rainfall fields may not directly match to weather station outputs. Rain rate in field 8 may be generated from the workaround if unavailable from your station. The daily total in field 9 is since rollover time, and available weather station outputs may need some processing in your spreadsheet to derive this. Some stations output a count of total rainfall, others the total annual rainfall, either of these may be used for field 11. Rainfall processing issues are frequently discussed in the Support Forum, so you may find the solution there or ask there for assistance.
The date that Cumulus first started tracking all-time records (<#recordsbegandate> see Webtags#Records), does not need to be updated for Cumulus 1 to recognise earlier monthly log files in its data subfolder and to use any monthly logs found in the various View and Edit options available from the Cumulus main screen.
Cumulus MX is different, it only reads monthly log files from the existing records began date, so that needs to be edited (StartDate= line in cumulus.ini with MX stopped, because it is not on any settings screen) to allow any earlier data to be read. You will also need to update all the other log files that record extremes manually using the editors provided in MX.
As <#recordsbegandate> is on the default Cumulus 1 or MX recordsT.htm template with the label "Records began on", inserting pre-Cumulus data implies you might want to amend that label wording on that template to indicate it is the date that Cumulus 1 was first operational, rather than the date of the earliest tracked highs and lows.
If you prefer to edit the start date and keep the recordsT.htm template label "Records began on" unchanged on the default in Cumulus 1 or MX, the method is to stop Cumulus 1, and amend the StartDate= line in cumulus.ini within the main Cumulus folder before re-starting Cumulus, but (in case you make a mistake) back up everything first!
Cumulus Wind Speed Terminology
How wind speeds relate to various weather stations is explained in FAQ. Basically there are 3 values processed by Cumulus:
- Gust - the highest wind speed over a particular period (this period defaults to 10 minutes),
- Average - the moving average of wind speed measurements over a particular period (this period can be set to what suits you, but defaults to 10 minutes),
- Latest - the most recent (wind speed or gust speed) measurement.
FAQ: Wind speeds in Cumulus with Davis stations, the EasyWeather differences in FAQ: Wind speeds in Cumulus with Fine Offset stations and FAQ: Wind speeds with Oregon Scientific and La Crosse stations
When Cumulus is running normally, it actually stores (in the fifth item after the date in each entry, column F in a spreadsheet) the highest (moving) average in the period since the previous logger record (assuming you have a) kept default averaging interval to 10 minutes, and b) have also adjusted the logging interval from the default 15 minutes to be 10 minutes).
If Cumulus is not running, it stores the average from the station logger, that is the latest reported moving average. For this reason the most accurate wind speed records are achieved if Cumulus is running all day every day.
Cumulus calculates the monthly/annual/period average wind speed (as used for 'This ...' screens in View menu and the NOAA report) by trawling through the relevant standard logs, summing the values for those individually logged average wind speed, and dividing by the number of entries for the required calendar days. It therefore assumes that each entry has equal 'weight', i.e. each one covers the same period. If your standard log(s) is/are a mixture of values stored while Cumulus is running and values copied from the station logger during periods when Cumulus was not running, then it is possible the two logging intervals have not been set to the same time, so the output value could be skewed for that month/year/period because of the difference in what was stored and the difference in the logging interval.
Windrun is also calculated from average wind speed measurements, in this case every minute if Cumulus is running, or from the values that are logged (at station logging interval) as average wind speed when Cumulus is restarted and catches up from the station logger. Again, if Cumulus is not left running the calculated value will be skewed.
List of fields in the file
The table is split by Cumulus version for all changes since version 1.8.5; it shows:
- The field number
- When this list was first produced, Cumulus 1 was all that was available and the decision then was to start with date in field zero to be consistent with index used for arrays in programming languages like JavaScript.
- Now that Cumulus MX is the main product, it uses field zero for the line number, and therefore date moves to field 1.
- For each field the equivalent letter that would be seen in a spreadsheet like Libre Office, Open Office, Excel etc is also shown in first column.
- As a quick guide to which fields can take signs and which can not accept decimal places, the second column indicates formatting rules.
- Any item labelled integer will not accept any decimal places. Any item labelled number can in Cumulus 1 take integer or decimal values, but in MX the decimal places are mandatory.
- Any item labelled unsigned will not accept a minus sign. Those labelled signed don't need + for positive, but need - for negative.
- The third column shows an example, and the values shown are sometimes integers and sometimes floating point numbers, and this depends on a number of factors, including your station type. If you are editing the values manually, you should use integers for humidity, wind bearings, and the two solar radiation figures, and floating point for the others (add a ".0" if necessary). Note that the figure varies depending on the units you select, and your weather station may not have all the sensors needed, in that case for you some figures will always be zero.
- The final column describes the observation often with a link to where there is more information.
Version 1.8.5:
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1(A) | Day-Month-Year (2 digits each) | 22/04/11 | Date as 2 figure day [separator] 2 figure month [separator] 2 figure year - the separator is that set in the your locale for short date format (see setup) |
| 2(B) | Hour-Minute (2 digits each) | 10:25 | Current time to nearest minute (no seconds allowed). Separator must be colon in MX, but can also be set to something else in Cumulus 1 |
| 3(C) | Signed number | 8.1 | Current temperature |
| 4(D) | unsigned integer | 96 | Current relative humidity |
| 5(E) | Signed number | 7.5 | Current dew point |
| 6(F) | unsigned number | 13.5 | Cumulus 'Average' wind speed over 10 minutes (or whatever period selected) (See #Cumulus_Wind_Speed_Terminology) |
| 7(G) | Unsigned number | 20.3 | Cumulus 'Gust' wind speed (See #Cumulus_Wind_Speed_Terminology) |
| 8(H) | integer | 138 | Average wind bearing (in degrees) |
| 9(I) | unsigned number | 7.2 | Current rainfall rate |
| 10(J) | unsigned number | 5.4 | Total rainfall today so far (i.e. resets to zero at daily rollover) |
| 11(K) | unsigned number | 30.10 or 998.2 | Current sea level pressure |
| 12(L) | unsigned number | 215.2 | Total rainfall counter (content depends on weather station type), might be rainfall total so far this year. This figure is not intended to be useful in itself, it may vary for no apparent reason. (It is used internally by Cumulus, but only within current meteorological day.) |
| 13(M) | signed number | 20.3 | Inside temperature |
| 14(N) | unsigned integer | 53 | Inside humidity |
| 15(O) | unsigned number | 17.6 | Cumulus 'Latest' gust (See #Cumulus_Wind_Speed_Terminology) |
| 16(P) | Signed number | 4.8 | wind chill (content depends on weather station type and Cumulus station settings) |
| 17(Q) | signed number | 8.1 | Heat index |
| 18(R) | unsigned number | 0.5 | UV Index (only valid if output by weather station) |
| 19(S) | unsigned integer | 197 | Solar Radiation (only valid if solar sensor on weather station) |
Added in 1.9.1
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20(T) | unsigned number | 0.08 | Evapotranspiration (only valid if output by weather station) |
| 21(U) | unsigned number | 171.88 | Annual Evapotranspiration (only valid if ET sensor on weather station) |
| 22(V) | Unsigned number | 3.4 | Apparent temperature |
| 23(W) | Unsigned integer | 663 | Current theoretical max solar radiation (see the FAQ on Solar max) |
| 24(X) | Unsigned number | 3.1 | Hours of sunshine so far today (only valid if solar sensor on weather station) |
Added in 1.9.2
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25(Y) | Unsigned integer | 158 | Current Wind bearing (See 7) |
For Cumulus MX editing a file created by Cumulus 1, any of the preceding fields that are not present will be defaulted to an empty string, but there will always be 50 fields (unless you are using MX version before 3.6.0, it which case MX cannot read the file.
Added in 1.9.3
For Cumulus MX 3.6.x reading a line created by Cumulus 1, all the remaining fields will be filled with exactly one space, and editing that to an empty string will be rejected. Cumulus MX before version 3.6.0 cannot read a log file with all lines in that log file created by any Cumulus 1 version prior to 1.9.4.
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 26(Z) | Unsigned number | 6.0 | RG-11 rain today (only valid if output by sensor) |
Added in 1.9.4
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 27(AA) | Unsigned number | 5.7 | Total Rainfall since midnight (this is for 0900/1000 'rollover' users; normally same as rain today for 'midnight rollover' users) |
Added in 3.6.0
| Field # | Rule | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 27(AB) | signed number | 13.7 | Feels Like temperature |
Example lines from the file
Note that your field delimiters may be different, and your date delimiter too.
An extract of a few lines of the file (v.1.9.0)
Here logging is quarter hourly, the field delimiter is a semicolon, the decimal separator is a comma, and the date separator a dash.
30-09-10;19:00;16,4;94;15,4;5,2;13,3;17;3,6;21,0;995,3;47,7;25,6;62;6,1;16,4;16,4;0,0;0 30-09-10;19:15;16,4;94;15,4;5,6;11,2;12;18,0;24,0;995,0;50,7;25,6;62;7,2;16,4;16,4;0,0;0 30-09-10;19:30;16,2;94;15,2;7,9;15,8;355;7,2;25,8;994,3;52,5;25,7;62;12,2;16,2;16,2;0,0;0 30-09-10;19:45;16,0;94;15,0;9,9;19,4;7;7,2;27,9;993,3;54,6;25,7;62;14,8;15,8;16,0;0,0;0 30-09-10;20:00;15,9;94;14,9;12,4;20,9;354;7,2;30,0;993,0;56,7;25,7;62;19,4;15,4;15,9;0,0;0 30-09-10;20:15;15,8;94;14,8;8,4;15,8;349;14,4;32,7;993,4;59,4;25,8;61;12,2;15,8;15,8;0,0;0 30-09-10;20:30;15,4;94;14,4;13,8;33,1;317;28,8;40,5;993,7;67,2;25,8;61;23,4;14,7;15,4;0,0;0 30-09-10;20:45;15,1;94;14,1;20,3;34,2;356;7,2;43,8;992,3;70,5;25,8;60;29,5;13,8;15,1;0,0;0 30-09-10;21:00;15,3;94;14,3;20,2;35,6;358;10,8;46,8;991,0;73,5;25,8;60;28,1;14,0;15,3;0,0;0 30-09-10;21:15;15,3;95;14,5;16,6;31,7;358;10,8;49,5;991,4;76,2;25,8;60;20,9;14,3;15,3;0,0;0 30-09-10;21:30;15,3;94;14,3;14,0;27,0;324;18,0;54,3;992,3;81,0;25,8;60;15,8;14,5;15,3;0,0;0 30-09-10;21:45;15,2;94;14,2;13,0;25,6;323;10,8;57,9;992,3;84,6;25,8;59;24,5;14,5;15,2;0,0;0 30-09-10;22:00;15,0;94;14,0;16,7;31,7;312;10,8;60,6;993,0;87,3;25,8;59;23,4;13,9;15,0;0,0;0 30-09-10;22:15;14,9;94;13,9;16,0;30,6;357;10,8;63,0;991,6;89,7;25,8;59;20,9;13,9;14,9;0,0;0 30-09-10;22:30;14,9;94;13,9;17,6;31,7;3;3,6;63,3;990,6;90,0;25,8;59;19,4;13,7;14,9;0,0;0
this is an example of a file from 1.9.1, with solar data:
Here logging is increased to every five minutes, the field delimiter is a comma, the decimal separator is a full stop, and the date separator is also a full stop.
22.04.11,10:25,8.1,96,7.5,13,20,138,0.0,0.0,1013.24,215.2,20.3,53,17,4.8,8.1,0.0,197,0.08,171.88,3.4,663,0.0 22.04.11,10:30,8.1,96,7.5,13,20,142,0.0,0.0,1013.28,215.2,20.2,53,11,4.8,8.1,0.0,216,0.08,171.88,3.3,673,0.0 22.04.11,10:35,8.1,96,7.5,12,18,142,0.0,0.0,1013.31,215.2,20.2,53,11,5.1,8.1,0.0,227,0.08,171.88,3.8,682,0.0
and from version 1.9.2:
Here logging is at the default interval, and the delimiters have their default settings for UK systems.
01/10/11,04:40,18.0,75,13.5,5.0,6.7,169,0.0,0.0,1021.4,885.3,24.4,61,5.6,18.0,18.0,0.0,0,0.00,0.00,17.5,0,0.0,158 01/10/11,04:50,17.9,75,13.4,4.5,9.5,169,0.0,0.0,1021.4,885.3,24.4,61,2.0,17.9,17.9,0.0,0,0.00,0.00,17.5,0,0.0,180 01/10/11,05:00,17.8,75,13.3,5.1,9.5,177,0.0,0.0,1021.2,885.3,24.4,61,7.5,17.8,17.8,0.0,0,0.00,0.00,17.2,0,0.0,180